Publications and News
Rigorous scientific research is at the core of what we do. Follow us here for publications, research updates and other news related to our work.

Healthy Aging Seminar at the Senior Day Out, Lubbock, TX, US
Dushani and Nipuni spoke to Lubbock area residents about the importance of nutrition, physical activity and brain health in July, 2024. They also spoke about how digital health technologies can help with improving older adult cognitive health, memory and learning.

Public session on healthy aging at Swastha by Link, Sri Lanka.
Dushani presented a public overview session on "Decoding Longevity and Healthy Aging" in partnership with Link Natural, the Sri Lankan company behind the famous wellness beverage "Samahan".
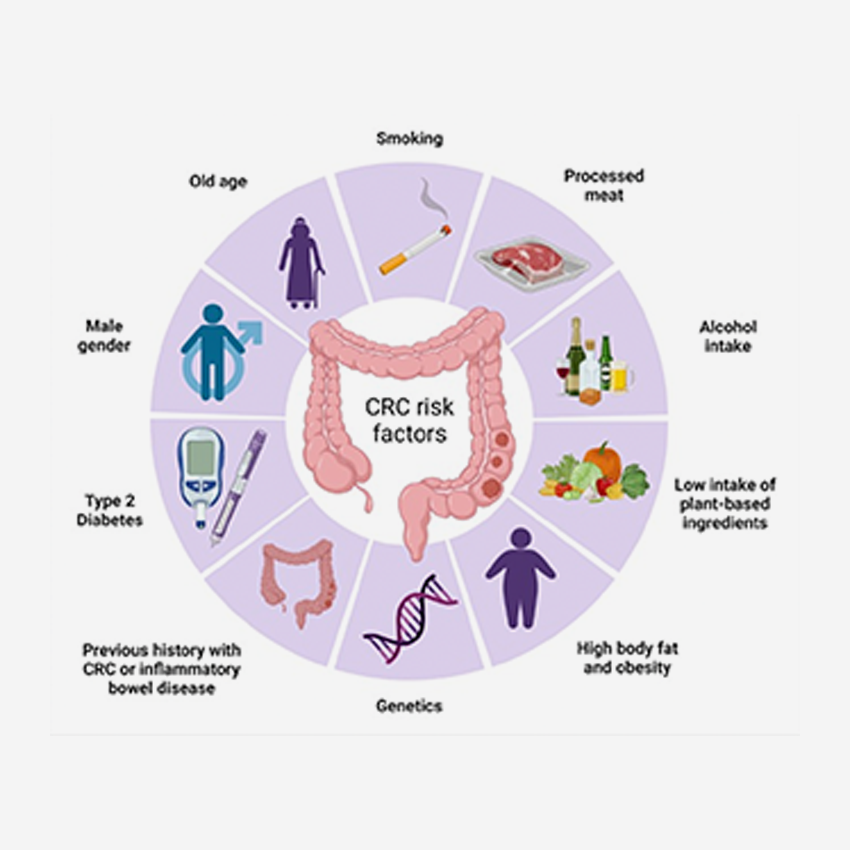
12th Annual Symposium on Global Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute (NCI) We presented a poster on colorectal cancer risk mapping at this symposium hosted by the National Cancer Institute (NCI)
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the United States and worldwide. Previous studies have identified several behavioral and biological risk factors of CRC, including lack of physical activity, smoking, alcohol use, poor dietary patterns, low physical activity, obesity and diabetes.

Elon University, NC Data Nexus event on "Women in Data". We conducted a session on Nipuni's journey from astrophysics to health data analytics and another session on how data can be leveraged to improved human health
Guest speaker Nipuni Palliyaguru from Texas Tech University spoke with the Department of Physics on Wednesday afternoon about her career path. Formally trained as an astrophysicist, Palliyaguru is accustomed to working with very large data sets – terabytes worth of data collected in a single night of observation. She recently co-founded a health analytics company, HealthSurveil, which aims to work with large sets of air quality data that may correlate to community health outcomes.

Texas Tech University Innovation Hub 2024 Accelerator Finalist
Listen to Texas Tech Accelerator Competition finalists pitch their innovative startups as they compete for entrance into the 2024-2025 Accelerator Program. The one-year program provides each startup team with a $25,000 grant, experienced mentors, access to the Innovation Hub's extensive network, and hands-on monthly workshops.

Texas Tech University Innovation Hub ILaunch Competition Finalist
Join the Texas Tech Innovation Hub for a night of fun as we cheer on aspiring entrepreneurs competing for a total of $20,000 in cash prizes! The iLaunch Competition and Awards Social will take place on Friday, November 17th.

Texas Tech Innovation Hub awards biotech, healthcare, and environmental technology startups funds to support their prototypes!
The Innovation Hub is proud to announce the recipients of the 2023 Prototype Fund. The four startups received a combined total of $55,000 to support the creation and development of their prototype.

Status, determinants and risk factors of all-cause dementia in South Asia: Findings from a preliminary analysis of global health data
South Asia is one of the most populous regions of the world. At present, South Asians make up more than 25% of the world’s population but little effort has been dedicated to studying trends and etiological factors driving aging and aging-related conditions in this part of the world. Even less characterization has been done on brain-related conditions, particularly all-cause dementia in South Asia.
Fasting blood glucose as a predictor of mortality: Lost in translation
Aging leads to profound changes in glucose homeostasis, weight, and adiposity, which are considered good predictors of health and survival in humans. Direct evidence that these age-associated metabolic alterations are recapitulated in animal models is lacking, impeding progress to develop and test interventions that delay the onset of metabolic dysfunction and promote healthy aging and longevity.

Sulforaphane Diminishes the Formation of Mammary Tumors in Rats Exposed to 17β-Estradiol
Elevated levels of estrogen are a risk factor for breast cancer. In addition to inducing DNA damage, estrogens can enhance cell proliferation as well as modulate fatty acid metabolism that collectively contributes to mammary tumorigenesis. Sulforaphane (SFN) is an isothiocyanate derived from broccoli that is currently under evaluation in multiple clinical trials for prevention of several diseases, including cancer. Previous studies showed that SFN suppressed DNA damage and lipogenesis pathways.

Frailty index as a biomarker of lifespan and healthspan: Focus on pharmacological interventions
Although survival has been the focus of aging research for many years, the field is rapidly evolving towards incorporating healthspan and health indices in studies that explore aging-related outcomes. Frailty is one such measure that is tightly correlated with human aging.

Combining a High Dose of Metformin With the SIRT1 Activator, SRT1720, Reduces Life Span in Aged Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet
SRT1720, a sirtuin1-activator, and metformin (MET), an antidiabetic drug, confer health and life-span benefits when administered individually. It is unclear whether combination of the two compounds could lead to additional benefits. Groups of 56-week-old C57BL/6J male mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD) alone or supplemented with either SRT1720 (2 g/kg food), a high dose of MET (1% wt/wt food), or a combination of both. Animals were monitored for survival, body weight, food consumption, body composition, and rotarod performance.

Perinatal diet influences health and survival in a mouse model of leukemia
The goal of the current study was to determine the role of maternal diet in the perinatal period on the health and survival of the offspring. AKR/J mice, a model described to be susceptible to leukemia development, was used where females were maintained on either standard diet (SD), high sucrose diet, Western diet, or calorie restriction (CR) as they were mated with SD-fed males.

Evaluation of 2-Thiothiazolidine-4-Carboxylic Acid, a Common Metabolite of Isothiocyanates, as a Potential Biomarker of Cruciferous Vegetable Intake
Cruciferous vegetable consumption is associated with favorable health outcomes. Bioactive compounds arising in these, especially isothiocyanates, exert effects that contribute to prevention of disease, in large part through the attenuation of inflammation and oxidative stress.

Isothiocyanates: Translating the Power of Plants to People
Isothiocyanates from cruciferous vegetables have been studied extensively in cells and in animals for their disease preventive and therapeutic effects. However, translating their utility to human populations has been both limited and challenging. Herein, clinical trials employing two isothiocyanates, sulforaphane (SFN; 1-isothiocyanato-4-(methylsulfinyl) butane) and phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC; 2-isothiocyanatoethylbenzene) that are isolated principally from broccoli and watercress, respectively, are summarized and discussed.

Withaferin A induces Nrf2-dependent protection against liver injury: Role of Keap1-independent mechanisms
Small molecules of plant origin offer presumptively safe opportunities to prevent carcinogenesis, mutagenesis and other forms of toxicity in humans. However, the mechanisms of action of such plant-based agents remain largely unknown. In recent years the stress responsive transcription factor Nrf2 has been validated as a target for disease chemoprevention. Withania somnifera (WS) is a herb used in Ayurveda (an ancient form of medicine in South Asia).

Frugal chemoprevention: targeting Nrf2 with foods rich in sulforaphane
Aging and growth of the world population, together with adoption of lifestyle factors such as smoking, obesogenic diets, and sedentary habits are escalating the global burden of cancer. According to World Cancer Report 2014, it is estimated that 8.2 million cancer deaths occurred in 2012 and that this toll will reach more than 14 million by 2030.
Global geographical overlap of aflatoxin and hepatitis C: controlling risk factors for liver cancer worldwide
About 85% of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC, liver cancer) cases occur in low-income countries, where the risk factors of dietary aflatoxin exposure and chronic hepatitis B and C (HBV and HCV) viral infection are common. While studies have shown synergism between aflatoxin and HBV in causing HCC, much less is known about whether aflatoxin and HCV synergise similarly.